Gym Workout with Tennis Elbow: Your Complete Guide to Safe Training and Recovery
Tennis elbow doesn't have to end your fitness journey. With the right approach, you can continue your gym workouts while managing lateral epicondylitis effectively. This comprehensive guide provides evidence-based strategies for maintaining your strength training routine while promoting healing and preventing further injury.
Also Read || Exercises for Arthritic Fingers Pain Relief
Understanding Tennis Elbow: The Anatomy Behind the Pain
Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, affects the tendons that attach your forearm muscles to the outside of your elbow. This overuse injury occurs when repetitive motions cause microscopic tears in the extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon, leading to pain, inflammation, and weakness in your grip strength.
The condition affects 1-3% of the population and is particularly common among weightlifters, office workers, and athletes who perform repetitive arm movements. Despite its name, tennis elbow is more often caused by occupational activities like lifting weights, using tools, or even typing than by playing tennis.
The pain typically develops gradually, starting as a mild ache on the outside of your elbow and progressively worsening over time. You may notice increased discomfort when gripping objects, lifting weights, or performing twisting motions with your forearm. Understanding this anatomy helps explain why certain gym exercises can either help or hinder your recovery process.
Safe Gym Workout Principles with Tennis Elbow
Prioritize Pain-Free Movement
The fundamental principle for training with tennis elbow is to work within pain-free ranges of motion. Research shows that some discomfort during exercise is acceptable, but sharp pain indicates excessive stress on healing tissues. Listen to your body and stop immediately if you experience acute pain that reproduces your elbow symptoms.
Modify Load and Technique
Reducing weight and increasing repetitions helps maintain muscle endurance while minimizing stress on the affected tendons. Perfect form becomes even more crucial when dealing with tennis elbow, as compensation patterns can worsen symptoms and delay recovery. Focus on controlled, smooth movements rather than explosive lifting techniques.
Choose Equipment Wisely
Recommended Exercises for Tennis Elbow Recovery
Eccentric Strengthening Exercises
Eccentric exercises, where muscles lengthen under tension, have shown superior results for tennis elbow rehabilitation compared to other training methods. These exercises promote collagen synthesis and tendon healing while gradually building tissue tolerance to load.
Eccentric Wrist Extension:
Sit with your forearm supported on a table, palm facing down
Hold a 1-3 pound weight and slowly lower your wrist over 5 seconds
Use your other hand to assist in lifting the weight back up
Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, 3 times per week
Supination with Dumbbell:
Hold a dumbbell vertically by one end while seated
Allow gravity to rotate your forearm into pronation
Control the movement and use your other hand to return to starting position
This targets the supinator muscle, often involved in lateral epicondylitis
Progressive Loading Principles
Upper Body Modifications
Continue training other muscle groups while modifying exercises that stress the elbow. Replace isolation movements with compound exercises when possible, and use neutral grip positions to reduce forearm muscle activation.
Safe Upper Body Options:
Neutral-grip pull-ups instead of chin-ups
Hammer curls instead of traditional bicep curls
Push-ups on an incline to reduce elbow stress
Exercises to Avoid During Recovery
High-Risk Movements
Avoid exercises requiring sustained hard gripping, as this increases tension in the common extensor tendon origin. When grip strength is necessary, use lifting straps or hooks to reduce forearm muscle activation during pulling exercises.
Equipment Modifications and Supportive Gear
Counterforce Bracing
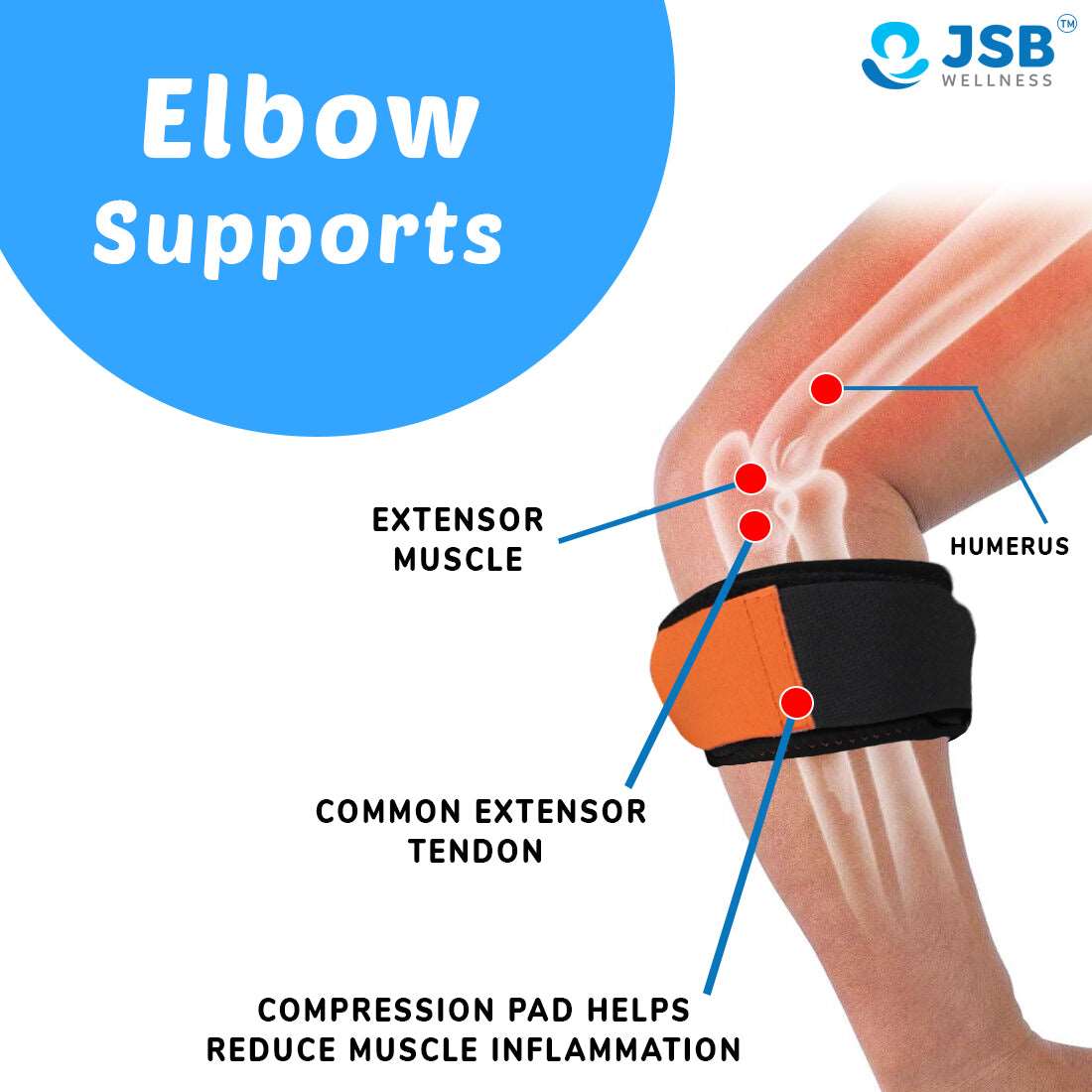
Tennis elbow braces can provide significant relief during workouts by redistributing forces away from the painful tendon insertion. These braces work by compressing the muscle belly and reducing tension at the lateral epicondyle.
Position the brace 2-3 inches below the elbow, ensuring the compression pad sits over the muscle belly rather than the bony prominence. Wear it during activities that typically cause pain, but remove it during rest periods to prevent dependency.
Grip Modifications
Using fat grips or padding can reduce the grip strength required for certain exercises. Alternatively, lifting straps and hooks can eliminate grip demands entirely for pulling movements, allowing you to train your back and biceps without stressing your forearms.
Temperature Therapy
Phase-Based Approach
Recovery typically follows three phases over 6-12 weeks. Phase 1 focuses on pain reduction and gentle range of motion. Phase 2 introduces light strengthening and stretching exercises. Phase 3 progresses to functional training and sports-specific movements.
Phase 1 (Weeks 1-2):
Pain-free range of motion exercises
Gentle stretching
Ice application
Activity modification
Phase 2 (Weeks 3-8):
Progressive strengthening exercises
Eccentric training introduction
Functional movement patterns
Gradual load increases
Phase 3 (Weeks 9-12+):
Sport-specific training
Return to full gym activities
Maintenance exercise program
Injury prevention strategies
Monitoring Progress
Track your pain levels, grip strength, and functional capacity weekly. Acceptable responses include mild muscle soreness that resolves within 24 hours and slight joint stiffness that disappears with warm-up. Warning signs include sharp pain during activity, persistent pain lasting 2-3 days after exercise, or pain that disrupts sleep.
Nutrition and Recovery Strategies
Anti-Inflammatory Support
Proper hydration supports tissue healing and helps maintain tendon elasticity. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly, as growth hormone release during deep sleep is crucial for tissue repair and recovery.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can impair healing and increase pain sensitivity. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or gentle yoga into your routine to support overall recovery.
Long-Term Prevention Strategies
Maintenance Exercise Program
Evaluate your daily activities for repetitive stress factors. Adjust your computer workstation, use ergonomic tools, and take regular breaks from repetitive activities to reduce cumulative stress on your elbow tendons.
Training Load Management
1. Can I still go to the gym with tennis elbow?
Yes, you can continue gym workouts with tennis elbow by modifying exercises, reducing weights, and avoiding movements that cause pain. Focus on pain-free exercises and prioritize proper form over heavy lifting.
2. How long should I avoid certain exercises with tennis elbow?
Avoid aggravating exercises for at least 2-4 weeks during acute phases, then gradually reintroduce them as symptoms improve. Most people can return to full training within 6-12 weeks with proper rehabilitation.
3. Are eccentric exercises really better for tennis elbow?
Research shows eccentric exercises provide superior pain relief and strength gains compared to concentric exercises, with a 10% better response rate for pain reduction. However, any strengthening approach is better than rest alone.
4. Should I completely stop lifting weights with tennis elbow?
Complete rest is not recommended as it can lead to muscle weakness and delayed recovery. Instead, modify your routine to work within pain-free ranges while avoiding exercises that aggravate symptoms.
5. Can I use a tennis elbow brace during workouts?
Yes, counterforce braces can be beneficial during workouts by reducing tension on the affected tendon. Position the brace 2-3 inches below the elbow joint for optimal effectiveness.
6. What weight should I use for tennis elbow exercises?
Start with 1-2 pounds and progress gradually based on tolerance. The goal is to perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions without increasing pain. Increase weight only when you can complete 30 repetitions on two consecutive days.
7. How often should I do tennis elbow exercises?
Perform rehabilitation exercises 3-5 times per week, with daily exercises during acute phases for stretching and range of motion. Strengthening exercises should be done every other day to allow recovery.
8. Can strength training actually help heal tennis elbow?
Yes, progressive strength training promotes tendon healing by stimulating collagen synthesis and improving tissue organization. The key is using appropriate loads and techniques that challenge the tissue without causing damage.
9. Should I use ice or heat before gym workouts?
Use heat before workouts to improve tissue pliability and range of motion. Apply ice for 10-15 minutes after workouts to control any inflammatory response and manage pain.
10. When should I see a healthcare professional for tennis elbow?
Seek professional help if pain persists despite 4-6 weeks of conservative management, if you experience numbness or tingling, or if symptoms significantly limit your daily activities. A physical therapist can provide manual therapy and exercise progression guidance.
Conclusion
Training with tennis elbow requires patience, modification, and a systematic approach to exercise selection and progression. By understanding the condition, implementing appropriate exercise modifications, and following evidence-based rehabilitation principles, you can maintain your fitness goals while promoting healing.
Remember that recovery is not linear, and setbacks are normal. Focus on consistent, progressive loading of the affected tissues while avoiding activities that reproduce your symptoms. With proper management, most people can return to full gym activities within 3-6 months and prevent future recurrences through ongoing maintenance exercises.
The key to success lies in listening to your body, modifying your approach as needed, and maintaining consistency with your rehabilitation program. By following the guidelines in this comprehensive guide, you can navigate your tennis elbow recovery while continuing to pursue your fitness goals safely and effectively.









Comments
Post a Comment